You are preparing to demonstrate your knowledge of wrist anatomy in a practical session for medical students. Your consultant has provided you with diagrams and images of the carpal bones, wrist structures, and relevant tendons. This station will test your ability to identify and explain the anatomy of the wrist.
Name the carpal bones 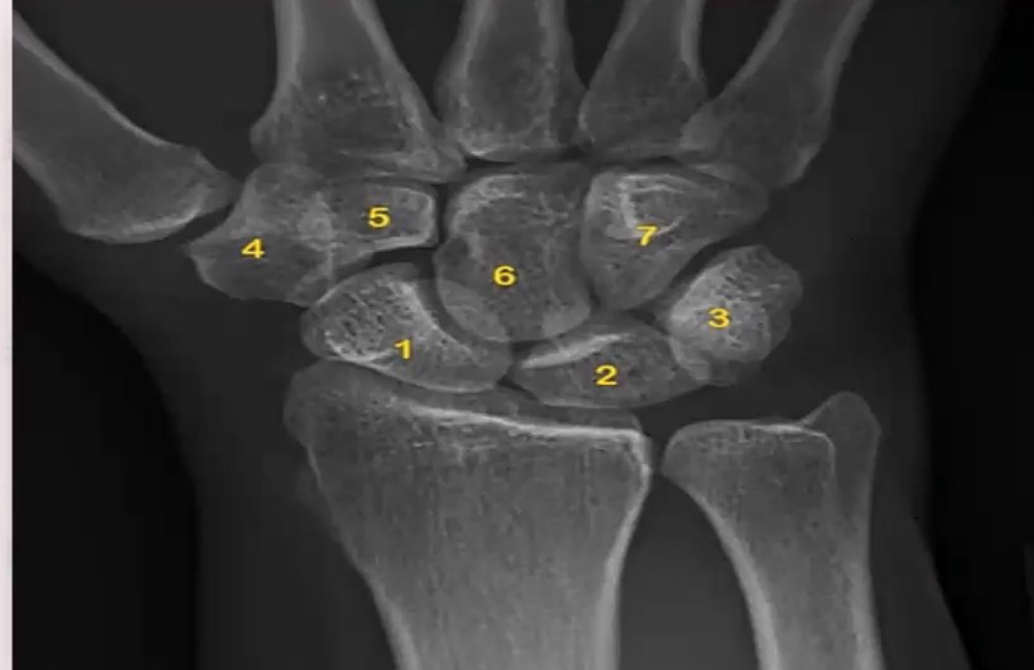
- 1: Scaphoid
- 2: Lunate
- 3: Triquetrum (overlain by Pisiform)
- 4: Trapezium
- 5: Trapezoid
- 6: Capitate
- 7: Hamate
Identify the following structures (Median nerve, Ulnar artery, Flexor retinaculum, Superficial palmar arch) 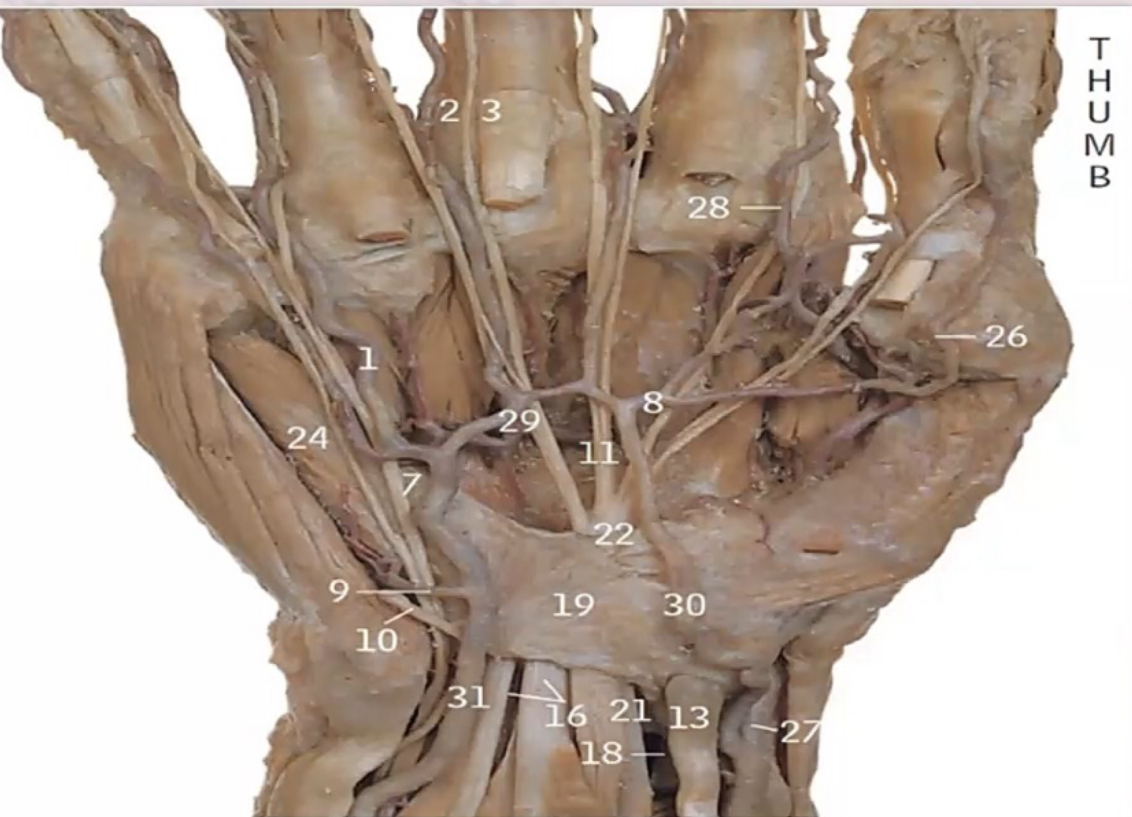
- 21: Median nerve
- 31: Ulnar artery
- 19: Flexor retinaculum
- 29: Superficial palmar arch
What are the structures passing through the carpal tunnel?
- Contents of the carpal tunnel:
- 4 tendons of Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
- 4 tendons of Flexor Digitorum Profundus
- 1 tendon of Flexor Pollicis Longus
- Median nerve
Show the thumb movements on your hand, and mention the muscles, and nerve supply of each muscle.
- Flexion
- Flexor pollicis longus: Median nerve
- Flexor pollicis brevis: Median nerve
- Adductor pollicis: Ulnar nerve
- Extension
- Abductor pollicis longus: Radial nerve
- Extensor pollicis longus: Radial nerve
- Extensor pollicis brevis: Radial nerve
- Abduction
- Abductor pollicis longus: Radial nerve
- Abductor pollicis brevis: Median nerve
- Adduction
- Adductor pollicis: Ulnar nerve
- Opposition
- Opponens pollicis: Median nerve
- Flexor pollicis brevis: Median nerve
- Abductor pollicis brevis: Median nerve
How to checking FDS & FDP function?
- FDP Test: Fix PIP joint, ask for DIP joint flexion.
- FDS Test: Fix adjacent digits, ask for flexion of the examined digit.
A patient with tenderness at the anatomical sunff box. You are shown this image. What is the diagnosis? 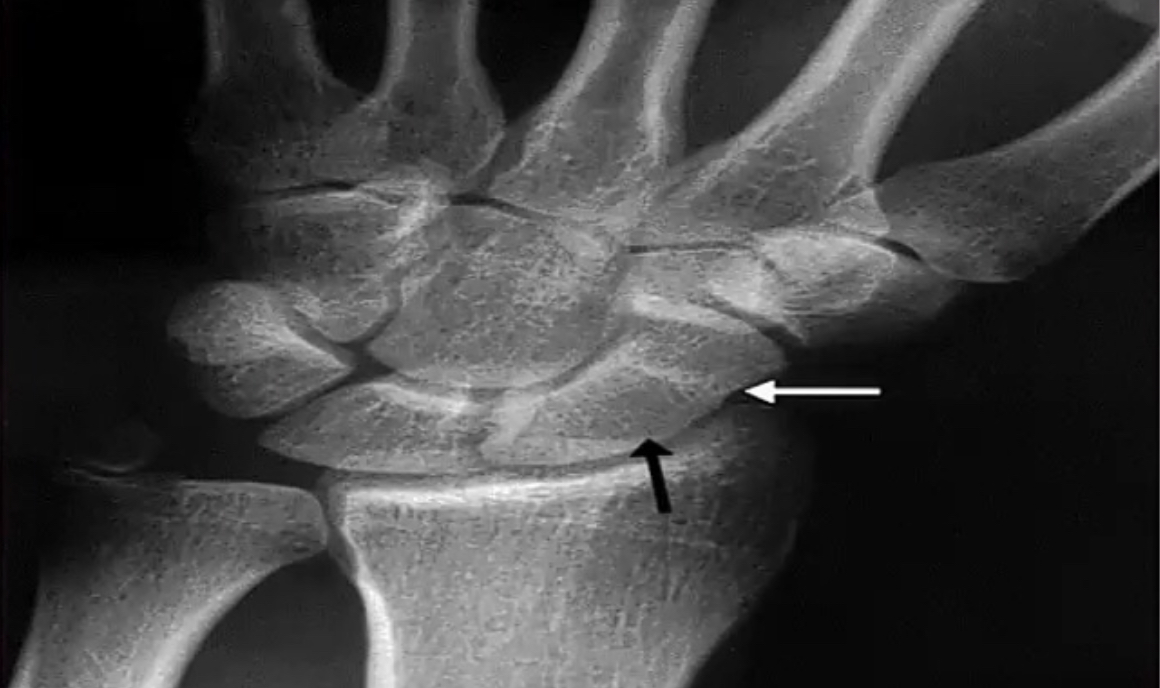
- Possible Diagnosis: Fracture of the scaphoid bone.
- Complications: Avascular necrosis, malunion, delayed union, nonunion.
Identify structure number 2. What is it’s significance? 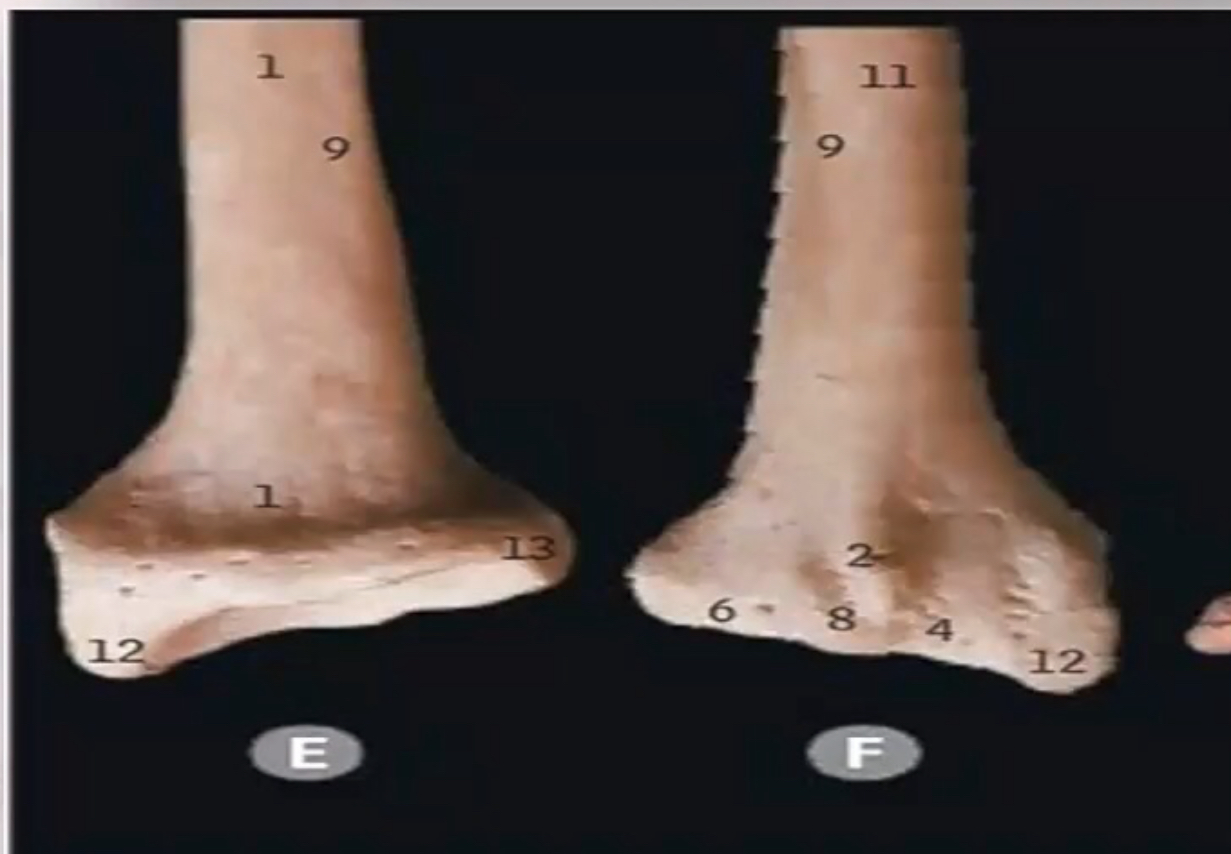
- Identification: Lister tubercle.
- Significance: Serves as a pulley for the tendon of the Extensor Pollicis Longus (EPL).
What are the attachments of flexor retinaculum
- Proximal: Tubercle of scaphoid, Pisiform
- Distal: Trapezium, Hook of hamate
What is the median nerve sensory distribution in the hand?
- Distribution: Lateral ⅔ of the palm, lateral 3½ digits on the palmar side, dorsum of the tips of index, middle, and thumb.
How to do Allen’s Test for ulnar artery?
- Procedure: Elevate hand, make a fist, occlude arteries, open hand, release ulnar artery, observe for color return within 7 seconds.
Identify the following structures (5,6,9,10,11,12,13)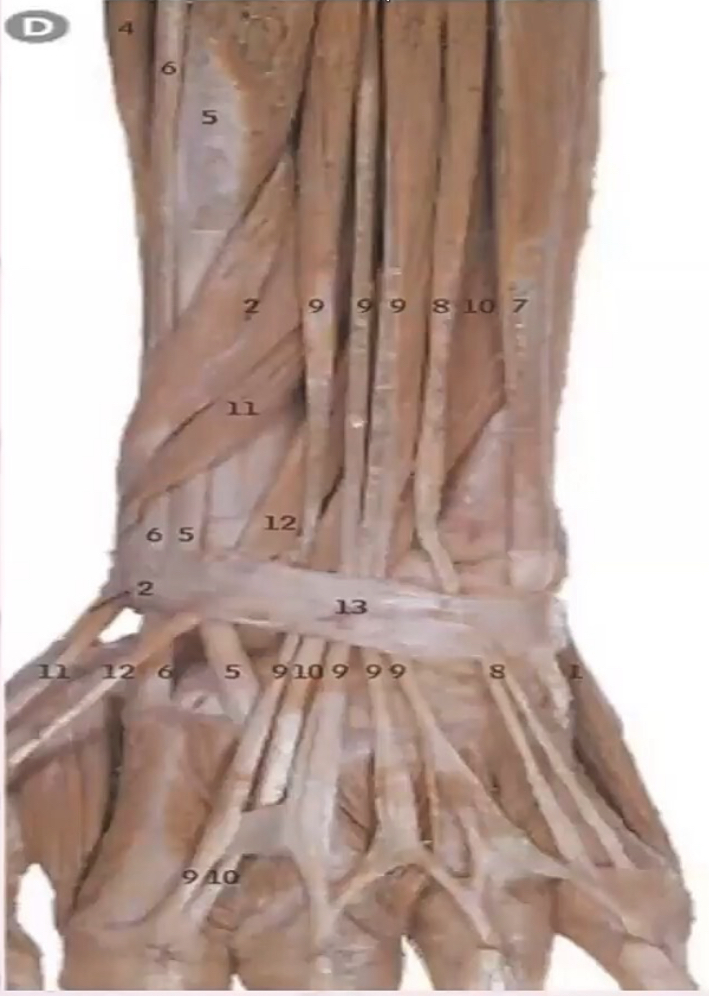 
- 5: Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- 6: Extensor carpi radialis longus
- 9: Extensor digitorum
- 10: Extensor indicis
- 11: Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
- 12: Extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
- 13: Extensor retinaculum
What is the insertion of extensor tendons?
- Insertion: Extensor expansion (extensor hood).
What is the Extensor Hood?
- Description: A triangular aponeurosis on the dorsum of the fingers where extensor tendons insert into the phalanges.
Course: Free Samples
